Disabling the Task Scheduler Service in Windows Server can be a necessary step in certain scenarios, such as when you need to minimize background processes to maximize system resources or for security reasons. The Task Scheduler Service allows users to automate tasks and programs on their systems: that said, if you find yourself needing to disable it, in this post we'll briefly explain how to do it safely.
The Problem
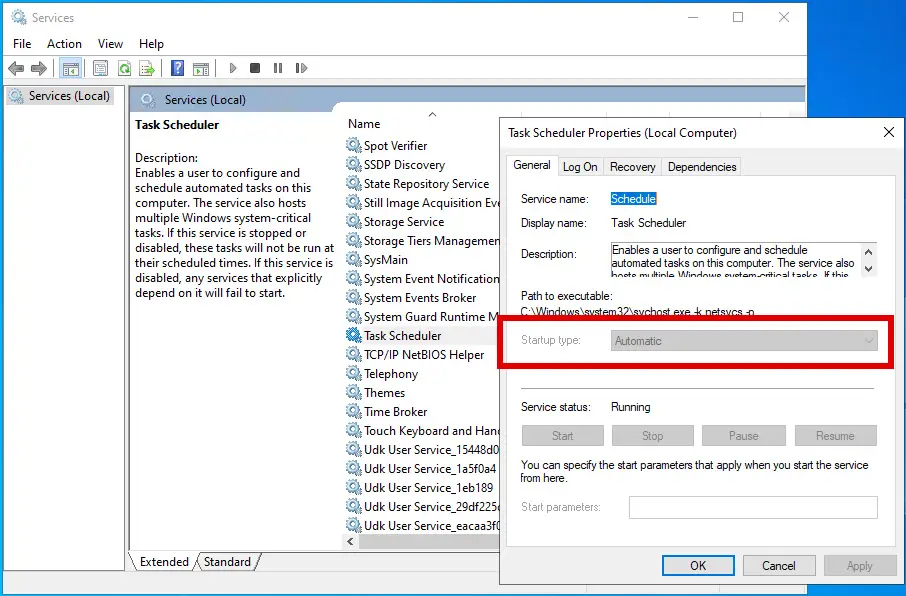
As you might already know, you can't disable the Task Scheduler Service using the Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services feature: if you try to do that, you'll find that the required options to disable it are greyed out, even for the local Administrator user:
For the same reason, we won't be allowed to disable it using the sc config Schedule start= disabled command from an elevated console prompt, or using a Group Policy.
The Solution
Luckily enough, there is an easy and viable workaround that we can use to fulfill our task that involves the use of the Windows' registry editor:
- Press Windows Logo + R on the keyboard to make the Run prompt window appear.
- In the Run prompt, type in regedit.
- Navigate to the following path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Schedule
- In the right pane, double-click on the Start key, and change its value from 2 (Automatic) to 4 (Disabled).
- Restart the machine to apply the changes.
If you need to re-enable the Task Scheduler Service at any point, simply follow the same steps outlined above, setting the Start key value to 4 (Automatic) instead of 2 (Disabled): remember to reboot the system to apply the changes.
Conclusion
We hope that our guide will help other system administrators looking for a quick and effective way to disable the Task Scheduler service on Windows machines.
However, it's important to keep in mind that disabling the Task Scheduler Service can have significant implications on automated tasks and programs on your server, so it's crucial to carefully consider whether it's necessary and to plan accordingly. Always ensure you have a backup plan in place and thoroughly test any changes in a controlled environment before applying them to a production server.